What is the Purpose of the Binocular?
Let’s start at the beginning of our Binoculars FAQ’s (Frequently Asked Questions) with what is their purpose. Binoculars are the ideal instrument to visually bring distant objects closer, magnifying these objects to better distinguish their details.
The situations in which binoculars are used are as varied as the objects observed. Among the activities where binoculars widely used are astronomy, ornithology, observation of nature and animals (e.g., safaris), or hunting and sailing.
The possibilities are practically unlimited; Binoculars are very practical, e.g., for traveling, hiking (especially in the mountains), sporting events (e.g., in a stadium), concerts, theater, and opera.
What Causes an Internal Focus?
Focusing is the “focus” of the image. In the case of the internal focusing, only the lenses move inside the binoculars. It is a closed system in which the suction of dust, air, or moisture is controlled.
What is the Near Point of Binoculars?
This number indicates the shortest distance to which objects can be sharpened and distorted without distortion. It can be essential to know, for example, when used in the museum to observe insects or the like.
What are BK-7, BaK-4, and SK15 Prisms?
- BK-7: Prism of boron crown glass. The standard for good imaging performance.
- BaK-4: Selected and carefully machined High-performance prisms made of barium crown glass allow an even better detail resolution and a brighter, color-contrasting image.
- SK15: Prisms made of high-quality SK15 glass are used in the farlux SELECTOR V. They enable the minimization of unwanted internal reflections and thus create a sharp image with the best contrast.
Why are Some Binoculars Nitrogen-filled?
Waterproof binoculars for all-weather applications are filled with nitrogen (N2) to avoid fogging of the inner optics during temperature changes.
Are larger Lens Binoculars Better?
A widespread belief is that the higher the magnification, the better the binoculars. However, this is not always true, because the quality of the glass material, prisms, coatings, and mechanics selected is essential to produce a high quality binocular.
Enlargement should be more appropriate. For most observing purposes, an 8 or 10 times magnification is entirely sufficient. If you stay in this magnification range, you can easily hold the binocular in your hand without being too shaky.
At higher magnifications (from 12-fold), this is not possible anymore. The whole picture shakes more and becomes blurred, so these binoculars need a tripod. Binoculars are available up to 20 times magnification.
If you prefer a high magnification, but want to do without a tripod, there is the possibility of buying binoculars with image stabilization.
If you prefer even higher magnifications, a spotting scope would be optimal. Spectra usually offer magnifications of 20 to 60 times, which can be adjusted using a zoom eyepiece. A tripod is also necessary here. In some cases, there is even a table stand included.
What are the Best Brands of Binoculars?
Among the top of the binoculars are the Leica and ZEISS brands. Which are undoubtedly the top of the range? Other brands of very high quality are Steiner, Minox, and Nikon. Representatives of the middle range are Eschenbach, Bushnell, and Bresser. That said, other brands also offer some binoculars that can be perfect for specific uses.
Why do You Need Binoculars at All?
Binoculars are an optimal device to visually approach distant objects by magnifying them so that the observer can see their details more clearly. Their applications are as varied depending on the interests of the observer.
Some classic areas of application are, astronomy, bird watching, nature and animal observation (e.g., Safari), hunting and sailing.
The fields of application are almost inexhaustible for travel, hiking (especially in the mountains), for sporting events, concerts, theater, opera, and for many other applications in everyday life.
What Does a Phased Treatment Mean?
Some high-quality binoculars are specified with phase processing, which is a special treatment layer applied to the roof prisms. When a light ray arrives on the prism in the roof, it is reflected several times taking the form of a roof ridge, and this reflection divides the rays into two segments, which causes a phase shift of the light waves.
In other words, the waves of light rays are no longer identical but shifted, and this has the effect of reducing the resolution as well as the contrast. Specific treatment layers are applied to correct the phenomenon described.
What Does it Mean When You Have 10×42 Binoculars?
All the binoculars have this code, and it indicates the magnification and lens opening characteristics of the binoculars concerned.
The first value is always the magnification, and in this case, it has a magnification of 10 times.
The second value specifies the opening of the lenses, always indicated in millimeters. Binoculars 10×42 have a lens aperture of 42 mm.
What is the Difference Between Porro Prism Binoculars and Roof Prisms Binoculars?
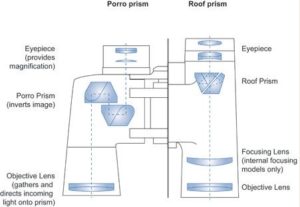 The difference between these two types of binoculars lies mainly in the implementation of different systems of prisms to straighten the image that was initially formed in reverse. Some are called prisms of Porro and the other prisms in the roof.
The difference between these two types of binoculars lies mainly in the implementation of different systems of prisms to straighten the image that was initially formed in reverse. Some are called prisms of Porro and the other prisms in the roof.
For simplicity, let us say that in the prisms of Porro, the light rays follow a path of rectangular form, whereas, in the prisms in the roof, this path is at an acute angle as the form of a roof. Today users have a small preference for roof-top binoculars.
These two types of binoculars are quite different in their shape. In the Porro, the gap between the two objectives is greater than between the two eyepieces. By comparison, roof systems have a more compact and narrow form, due to the different designs of the prisms.
Porro’s binoculars have a reasonably broad shape, but their advantage lies in the great relief effect they give to the image. The focusing system is of the exterior type in the Porro, while it is located inside the tube in the roof prism binoculars.
This latter type of focus is often preferred to that of the Porro because it allows a more robust construction and better protection against moisture. One can not say that one system is better than the other.
For each type, there are binoculars of good quality and lower quality. That said, manufacturing a good pair of roof prism binoculars is much more complex. It is therefore recommended, for the bottom of the range, to look more closely and to be advised.
How Do I Keep My Binoculars Clean?
Binoculars are not merely decorative objects exhibited in a showcase, but a practical instrument for use in the field for all sorts of observations. They inevitably become dirty.
Externally, one can easily wipe them with a cloth while cleaning the glasses requires a little more precaution. The glasses have received anti-reflective treatments, and this sensitive layer risks damage by too vigorous cleaning. Here is the first principle in cleaning: as little as possible.
On the other hand, it is possible to pass a soft brush on the glasses regularly, to remove grains of dust carefully. If the lenses are seriously dirty, then it is necessary to proceed in other ways and consider a more intense cleaning.
The best way is to use a microfiber fabric or other very soft fabric. Make sure there are no large dust particles trapped in the fabric, then you can wipe the glasses gently, preferably by circular motions. Dry cleaning may not be sufficient. In this case, we offer a specific liquid that allows you to perform efficient and non-aggressive cleaning.
For maximum protection, it is better to replace the caps on the glasses after each use of the binoculars.
How Big Should the Facial Field be in Binoculars and Are There Big Differences?
A large field of vision with binoculars is always an advantage. The human eye has a facial field of 180 ° through the fusion of the visual impressions of both eyes.
However, this is not possible with binoculars. Nevertheless, an attempt is made to get as large a facial as possible. The magnification and the eyepieces are decisive for a binocular.
The smaller the magnification, the larger the facial field. Also, wide-angle eyepieces can be produced using special eyepiece construction, despite higher magnification; a wide facial field can be achieved.
But here you have to careful as some binoculars offer large facial surfaces, but the edge sharpness drops in the last third of the field of view. Good binoculars have a sharp, sharp field of vision.
In the technical data, the visual fields are indicated at a thousand meters, e.g., 56m / 1000m. This means that one sees a field of view of 56 meters wide at a distance of a thousand meters.
This is sometimes also indicated in angular degrees. With these conversion formulas, one can calculate the data itself. The factor 17.5 is the field of view in meters with a facial field of 1 °.
Visibility at 1000m = degree (real) x 17.5
Degree (real) = visual range at 1000m / 17.5
Are Good Binoculars Necessarily the Ones with the Highest Magnification?
It is indeed a widespread belief, but this is not true because what determines the quality of binoculars is the choice of materials for lenses, prisms and treatments, and also mechanical performance. As for the magnification, we should instead choose it according to the field of use of the binoculars.
For most users, a magnification of 8 or 10 times is sufficient. While remaining within this magnification range, one can very well use the freehand binoculars, without seeing the image tremble too much. If the magnification is stronger (from 12 times), this will not necessarily be the case.
The image will shake more, and you will get the impression that it is blurry. The only solution then is to mount the binoculars on a tripod. Binoculars are available with up to 20 times magnification.
If you prefer a high magnification but do not want to use a tripod, you can buy binoculars with image stabilization. If you wish to have even further magnification, then it is a telescope that you should choose.
Most spots offer magnifications of 20 to 60 times, adjustable with a zoom eyepiece. Of course, a tripod is also essential, and some spots are provided with a tabletop tripod.
Is it Worth Paying a High Price for Binoculars, or Can You Find Inexpensive But Still Good Quality Binoculars?
It’s like everywhere: one who puts more money gets better quality. But it is true that today, we can manufacture low-cost instruments of almost acceptable quality.
However, if you are not prepared to make some significant compromises regarding chromatic aberrations, contrast, sharpness, transmission, and rendering true to reality, you must necessarily turn to more expensive binoculars.
High-quality instruments require complex work regarding optical and mechanical performance to eliminate as many aberrations as possible. This also applies to the mechanical focusing system, which must be of good quality, since the pleasure of observing may not last if the focus moves too much or remains stuck.
As for the eyecups, these are essential elements for comfort, and this is where you should not make big compromises either. There are available rigid eyelets that can be expanded by rotation and offer several locking positions.
How Can One Test the Quality of a Pair of Binoculars?
At first sight, the quality of a pair of binoculars is not easy to determine. If you look at the landscape in good weather, you will not necessarily notice the differences between the models.
Beyond the optical system, it is also necessary to look at the focusing mechanism and the optical tube itself.
For example, you can hold the instrument under a white neon tube and check the anti-reflection treatment. It is clear whether the objectives have a color that is usually green or violet. If you see white reflections, the glasses are not treated, which means that a precious part of the light is lost before reaching our eye.
It is advisable to do the same test with the eyepieces. Indeed, some manufacturers of low-end binoculars do not apply the coating. In addition to the loss of light, untreated glasses would cause many reflections, a disadvantage to avoiding at all costs.
Then, the binoculars can be held facing a clear surface at a certain distance. Two small white discs should appear in the eyepieces; These are the exit pupils. They should be round and not angular. If they have angles, it is because the prisms can’t reflect all the light. It would be a major aberration that would degrade the quality of the image enormously.
Then we can try to make a contrary observation. If the binoculars are of lower quality, it is quite possible that reflections appear in the field of view, which greatly reduces the contrast of the image. To eliminate these reflections, the interior of the binoculars should be blackened matt.
One should also ensure the purity of the colors.
For this purpose, the binoculars can be directed towards a white wall illuminated by the sun. Colored fringes may then be detected. If they are too large, they may affect the quality of the image. So, optics producing pure colors will always be an asset.
Several manufacturers offer binoculars with ED glass lenses or fluorite lenses. These models have almost no chromatic aberration, which is particularly important for high magnifications.
Observing the night sky is a good way to test binoculars because it often reveals image defects.
It is enough to aim at a star or a brilliant planet, or even the moon, to be able to form an idea.
The focus is focused exactly on the object at the center of the image, and the object is shifted to the edge of the visual field.
It is then that one can see possible defects, for example, distortions of the star at the edge of the image, or an insufficient peripheral sharpness. If the image field has curvatures, it is also there that they will be detected. An image defect will be noticed all the more as the lens is large.
Image Stabilizer: Is it Worth Choosing Binoculars That Offer This Function?
Binoculars with image stabilization are interesting when using high magnifications without wanting to mount the instrument on a tripod.
Moreover, people whose hands tremble easily will have every interest to acquire this type of binoculars in which electronic sensors compensate for the slightest tremors.
It is thus possible to maintain perfectly still binoculars offering a magnification of 15 times. The image appears extremely sharp, as any tremor has been neutralized.
I Have Some Zoom Glasses on Offer. Is this is A Better Variant, so I’m not limited to a Fixed Magnification?
Zoom binoculars are very handy because they offer the possibility to adjust the magnification infinitely. So you are armed for many observation purposes. But an observation through such glasses also always represents a compromise.
The additional lenses, which are decisive for the zoom function, have poorer quality than a glass with a fixed focal length. This does not affect sunny daylight, but if there are severe contrast ratios, dusk or night.
Most zooming glasses show a tunnel effect, which is usually particularly strong at low magnification. You have the impression of viewing the image through a long black tunnel. Only a few field puzzlers with zoom functions do not show this effect.
I Am Looking for Binoculars for Water Sports, What Do You Recommend?
 For water sports, you should choose strong binoculars that, in addition to a good optical system, offer great mechanical strength.
For water sports, you should choose strong binoculars that, in addition to a good optical system, offer great mechanical strength.
A complete rubber cladding is recommended so that the instrument does not escape from the hands too easily. Binoculars intended for water sports will preferably be watertight under pressure. This is the case for many models, up to a depth of 5 meters.
It is also preferable that the instrument is filled with nitrogen, which prevents the entry of moisture and the appearance of fog inside.
If also, you equip your binoculars with a neoprene lanyard, they cannot sink in case they fall into the water.
I’m Looking for Binoculars That I Can Take On a Mountain Hike. What do you recommend?
For mountain hikes, it is recommended to choose binoculars that are not too heavy. In any case, we already have a lot of weight to carry; So it is better not to add again with the binoculars and settle for a standard model of 10×42.
This type of binoculars, which weighs about 700 grams, is light enough to be worn easily, but it still allows observation at dusk. If you prefer an even more compact instrument, you can choose a 10×25 model.
This type weighs only about 300 grams and easily enters a pocket of trousers. However, these binoculars are not very bright (AP 2.5 mm); they should be used only in daylight.
Apart from the opening and the magnification, the important factors are the treatment of the lenses and the prisms as well as the choice of the glass; this is what determines the great differences in quality.
Which Eyecups Should you Choose?
The eyecups play an important role if the parasitic light is to be avoided. There are soft rubber eyecups and hard plastic eyelets.
The hard eyecups, retractable by turning them, have the advantage of being very durable and often present several stops to block their position.
The rubber eyecups are more flexible and can be folded as needed. But with time, they can become brittle, because the softening agents disappear by volatilizing.
Are There Binoculars That Are Not Only Made for the Day or Night but All Situations?
There is what is called standard binoculars that are suitable for almost all light conditions.
The 10×42 or 8×42 models, for example, are standard binoculars with a lens aperture of 42 mm and a magnification of 8 or 10 times, respectively.
The essential criterion is what is the luminosity of the instrument; in other words, how much light arrives on the eye. In 8×42 mm binoculars, the light beam reaching the eye has a diameter of 5.25 mm.
It is enough to obtain, even at dusk, a clear image and sufficient stimulation of the retina. This type of instrument makes it possible to observe animals at dusk or sunrise. Even in the middle of the night, it will still be usable, but not necessarily the ideal.
What counts in these binoculars is to have an optical system as good as possible. This will differ depending on the type of glass used, the processing, and the reflection capacities of the prisms.
I Am Looking for Binoculars to Observe the Birds, but Which Ones are Suitable for This?
 True color rendering is an important factor in the choice of binoculars for bird watching, as we would like to see the colors of the plumage as they are. It is, therefore, advisable not to choose the least expensive models, but those that offer a high-quality optical treatment.
True color rendering is an important factor in the choice of binoculars for bird watching, as we would like to see the colors of the plumage as they are. It is, therefore, advisable not to choose the least expensive models, but those that offer a high-quality optical treatment.
If prism binoculars are chosen, these prisms should not be covered with a single layer of silver but have a large number of dielectric layers. They should also have received what is called a phased treatment that prevents the phase shift of the light waves passing through the prism.
If you choose pocket binoculars, look carefully at the eyepieces to see if they are suitable for eyeglass wearers, if necessary. When all these factors are combined, the binoculars will offer maximum clarity, contrast, and color fidelity.
I Would like to Mount Binoculars on a Tripod. Which One Should you Choose?
Most binoculars can be mounted on a tripod. In general, it is sufficient to unscrew a cap located in front of the central bridge and behind which hides a 1/4 inch screw pitch.
The binoculars can then be attached to a tripod using an adapter. However, you have to think carefully before making your choice. Indeed, it is useless to mount binoculars weighing 1 kg on a small light aluminum tripod.
The tripod would be heavily overloaded, and the binoculars would move as much as they touch. Wishing to observe in such conditions would make no sense.
As a general rule, tripods are made of aluminum, wood, or carbon. The aluminum is very light and easily transmits vibration, so it is necessary to have a good thickness of material and a very solid central structure. Wood transmits less vibration, and Ashwood is used. In addition to the thickness of the material, the weight of the tripod is important to ensure good stability.
On some tripods, the load limit is indicated. If the weight of the binoculars corresponds approximately to this load limit, it would be better to choose a tripod of the higher category.
I Would Like to Mount My Binoculars on a Tripod, Which One Should You Choose?
If you want to observe with binoculars while wearing glasses, it is important that the binoculars are designed for this purpose. However, manufacturers do not always indicate this characteristic.
Some binoculars are not suitable for viewing with glasses because they would show a very small and cut visual field.
The main point: the exit pupil must be located further back, at a distance of approximately 20 mm from the eyepiece, to allow the wearer of the spectacles an optimal aim. Moreover, the eyecups must not be disturbing.
There are already many models on which one can retract the eyecups by turning them. These are made of hard plastic. There are also flexible eyecups that can be folded. They place themselves gently against the eye; however, as the softening agents volatilize over time, the eyecup may become brittle.
What Does Anti-reflective Treatment Mean?
This term refers to a set of thin layers which are applied in the vapor phase to optical glasses under a high vacuum atmosphere. The aim is to minimize the reflections on the lenses and thus increase the transmission of light.
These layers are often made of magnesium fluoride; Their thickness and their refractive index are decisive for the reduction of reflections. In this process, light interference must neutralize each other.
More often than not, we apply not only one but several layers (up to seven, or even more), to ensure a good reduction in reflections for the entire light spectrum. Anti-reflective treatment is recognized by its coloring, usually green or purple.
These colors are also called residual reflections. Make sure that the binoculars have the “multi-coated” indication, which indicates the multilayer processing.
What Are the Essential Points to Consider When Buying Binoculars?
Eyeglass wearers should ensure there binoculars have excellent eye relief. It is crucial to have ample clearance (about 20 mm), which allows you to see the entire visual field without vignetting, even with your glasses on your nose.
People with mild vision problems should be aware of the presence of an adjustable eyepiece. On this point, it is important to know to what extent the eyepiece can adapt to the eye’s lack of vision, and if the eyepiece adjustment can be blocked to avoid unintended modification.
This is an essential quality and can be verified immediately after a purchase: When directing the binoculars towards a white surface located at about 30 cm, it is necessary to see a circular white surface that does not darken towards the edges. This is your guarantee that all the light passing through the eyepiece reaches your eye.
Other quality criteria arise only after a certain period of use of the instrument. If the binocular is of poor quality, then the optical adjustment of the prisms is unsatisfactory, and this can lead to headaches after relatively long observations. It is also possible to obtain double images.
An essential quality criterion for binoculars is the anti-glare treatment of lenses and prisms.
Normal optical lenses reflect part of the incident light, resulting in loss of brightness and loss of contrast. The treatment of lenses (so-called vapor phase application of a mineral layer) significantly reduces reflection and increases light transmission.
What are the Essential Points to Consider When Buying Binoculars?
WP – means “waterproof.” The waterproof binoculars have specific seals, and the pores are impregnated in a complex way.
Also, the vacuum inside the instrument is filled with nitrogen, so that water can not penetrate the binoculars.
These models are particularly suitable for all activities under varying weather conditions, such as sailing or mountain hiking.
B – (on German models) means “suitable for wearers of spectacles”; Namely, the binoculars have a large eye relief allowing us to see all the visual field without vignetting, even when wearing glasses.
G, GA, or RA – means “rubber-armed.” The rubber sheath protects the binoculars against shocks and splashes of water.
CF – sometimes means “Central Focus.”, but sometimes also “Close Focus”
“Central Focus” means a central focus. In Porro prism binoculars, the eyepieces are connected by a bridge that can be moved forward and backward using the central focusing wheel.
“Close Focus” means that the minimum focusing distance is very short, usually between 2 and 4 m, while on “normal” binoculars, focusing is only possible from a distance of 5 meters.
When we like to observe small or very close objects like Butterflies or birds, we need a short minimum distance, because otherwise, the instrument does not allow development.
W, WF, WW, or Wide – means “wide-angle” or “wide-field”; they are therefore binoculars offering a very wide field of view.
MC – means multi-coated processing. Since all good-quality binoculars are multi-layered, this is not always explicitly indicated in the model type.
UC – means “ultra-compact” and therefore designates particularly compact and lightweight binoculars (usually aluminum or sometimes also titanium).
HP – means “High Eyepoint.” These binoculars offer a large opening at the exit pupil.
D – (on German models) means “prisms in the roof.”
IS – stands for “Image Stabilization.” These are binoculars with image stabilization, which are used mainly by ornithologists and other observers of nature.
I hope the above Binoculars FAQ’s has helped you become more knowledgable about all aspects of binoculars.
Leave a Reply